Total Pageviews
Thursday, September 18, 2025
Thursday, July 31, 2025
Tuesday, July 29, 2025
Oracle Hyperion Planning
Monday, July 28, 2025
Essbase Backup
Essbase Backup
Backup
To prevent data loss, we use backup and recovery. You take of backup of data base so that when any miss happening accord. You can get back your data. There are many type of database backup.
Types of backups
1. Hot Backup: Perform backup while server is up and running mode.
2. Cold Backup: Perform backup while server is not in running mode.
Calc Scripts
What is a calculation script?
Series of commands, equations, and formulas that control calculation of the database
Text files with a .csc extension.
/* Creates Initial Budget */
SET UPDATECALC OFF;
CLEARDATA Budget;
Budget = Actual * 1.1;
CALC ALL;
=============
1. What is the difference between Calc Dim and Calc All?
Calculating Dimensions
*Aggregate one dimension and calculate its formulas:
CALC DIM (dimension);
*Aggregate all dimensions and calculate all formulas:
CALC ALL
2. What is the difference between Calc All and AGG?
Calculating Dimensions
*Aggregate all dimensions and calculate all formulas:
CALC ALL;
*Aggregate a sparse dimension:
AGG (dimension);
3. Clear Data
*Clear dynamic calc and store members:
CLEARBLOCK Dynamic;
Upgradation, Migration- Oracle EPM, Oracle EPBCS, Hyperion
Difference Upgradation- Migration
|
Upgradation-
Oracle EPM |
Migration |
|
1.
Upgradation: moving to a newer version of the same software. |
Migration: Process of copying all Application instance
form Operating environment to another. |
|
2. Example: Upgradation from Hyperion
9.x to 11.x |
Planning
11.2.x to Oracle EPBCS (On premise to Cloud) |
|
3.System:
same System, newer version. |
Different system |
|
4. Data: Preserved. |
Requires careful Migration. |
|
5. Complexity: Less complex than
Migration. |
More Complex. |
|
6. Focus: new features. |
Moving to Environment. |
|
|
Thursday, July 3, 2025
Thursday, June 26, 2025
Oracle EPM Job Market
Oracle EPM Hyperion Job Market
Wednesday, June 25, 2025
Oracle EPBCS Beginners
Oracle EPBCS (Enterprise Planning and Budgeting Cloud Service)?
EPBCS has world-class budgeting and forecasting, data management, and analysis capabilities in Oracle Hyperion Planning
- Oracle EPBCS Overview
- PBCS vs EPBCS
- Hyperion Planning vs Oracle PBCS/EPBCS
- EPBCS Basic Questions
- EPBCS Interview Questions
======Related Links====
Tuesday, June 3, 2025
Loading Data using Rules file, Free form method, Excel lock& send methods.
To load data into the database, we must build all dimensions first. The data will be loaded into a
page file, and indexes will also be created. When the page file reaches 2 GB, it creates another file
, and so on. Same with the index file. The files are created in the following path.
ARBORPATH/APP/app-name/db-name/ESS00001.PAG
ARBORPATH/APP/app-name/db-name/ESS00001.IND
Loading data can be done using any of the following methods.
1. Loading data using a rules file
2. Free-form data loading
3. Through Excel Lock and send (or through analyzer
Build the Dimensions using the Rule File
Build the Dimensions using the Rule File.
RULES FILES: Rules files are used to build the dimensions and to load data into Essbase database.
* Rules files are stored with.RUL extension on the server.
* To create the rules file, right-click on the rules file and click Create Rules file.
Building Dimensions using Rules files: We can create the hierarchies in the outline manually or
using rules files. There are 3 ways to build the rules files.
1. Generation reference method
2. Level reference method
3. Parent-child reference method
Sunday, June 1, 2025
Glossary Essbase
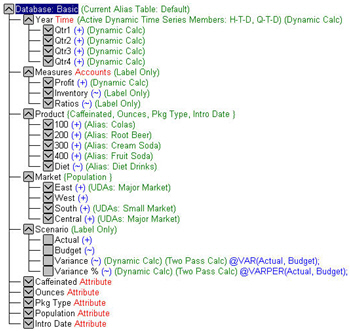
Application is a folder structure that contains one or more databases and related files.
Database is a folder that contains objects such as outline, rules files, calculation scripts, report scripts, and multidimensional data.
Outline: An empty outline is created as soon as the database is created. Double click on the
outline and click Add children to add dimensions. Outline consists of Hierarchies.
Dimension: consists of members. A hierarchy is nothing but a structural relationship among members. It gives parent parent-child relationship among members. The outline will also give consolidation operators.
Note: The name of the outline can be changed only by renaming the database. The name of the outline
cannot be changed directly.
Parent is a member that has a branch below it.
Eexample, Margin is a parent member for Sales and Cost of Goods Sold.
Child is a member that has a parent above it.
Example: Sales and Cost of Goods Sold are children of the parent Margin.
Siblings are child members of the same immediate parent, at the same generation.
Example: Sales and Cost of Goods Sold are siblings (they both have the parent Margin), but Marketing (at the same branch level) is not a sibling because its parent is Total Expenses.
Descendants are all members in branches below a parent.
Example: Profit, Inventory, and Ratios are descendants of Measures. The children of Profit, Inventory, and Ratios are also descendants of Measures.
Ancestors are all members in branches above a member.
Example: Margin, Profit, and Measures are ancestors of Sales.
The root is the top member in a branch. Measures is the root for Profit, Inventory, Ratios, and the
children of Profit, Inventory, and Ratios.
Leaf members have no children. They are also referred to as detail members, level 0 members,
and leaf nodes.
Example: Opening Inventory, Additions, and Ending Inventory are leaf members.
Generation refers to a consolidation level within a dimension.
A root branch of the tree, i.e., Dimension, is generation 1. Generation numbers increase as you count from the root toward the leaf member.
Levels refer to a consolidation level within a dimension. The leaf member is at Level 0, and the
parent member of level 0 is at level 1, and so on
Create Application, Database
Application, Database Creation- Essbase
An application is a folder structure that contains one or more databases and related files.
To create an Application, log on to the Essbase server using the EAS console (Through the EAS server).
- Double-click on the Essbase server
- Right-click on the application
- Click Create new application.
- Enter application name.
The application name can take a maximum of 8 characters.
DATABASE: A database is a folder that contains objects such as outlines, rule files, calculation scripts, report scripts, and multidimensional data.
To create a Database,
Double-click on the applications and right-click on the database. Enter the Database name. The
The database name can take a maximum of 8 characters for non-Unicode applications.
==================
Friday, May 30, 2025
Calculations- Essbase
CALCULATIONS- ESSBASE
BLOCK SIZE
Block Size: It is
the multiplication of the store Dense
Dimension Member (DDM) from each Dimension *8 bytes.
A- Dense
A1- Store
A2- Store
Total Dense Members: 2
B- Dense
B1- Store
B2- Store
B3- Store
B4- Store
Total Dense Members- 4
Block Size:
2*4*8 Byte=64 Bytes
Dimension types
Types of Dimensions
Note:
Attributed Dimensions are below the Standard Dimension.
Types of Dimensions: Standard Dimensions, Attributed Dimensions.
I. Standard Dimensions (SD)
Types
of Standard Dimensions
1. Sparse (Default) - Low Probability Ex: Root bear
2. Dense-
High Probability, Ex: Pepsi
* Not
Associated with Attribute Dimension.
|
Consolidation
Operation. |
No- Two pass |
|
Sparse, Dense
|
Required Storage Space |
|
Standard Dimension above Attributed Dimension. |
Storage Property- all |
|
Formula |
UDA allowed |
|
Shared Members |
|
II. Attribute Dimensions
|
Should be associate to Standard Dimension with Sparse. Not
Associated with Dense. |
Two pass |
|
Should be associate to Standard Dimension with Sparse. Not
Associated with Dense. |
No formula |
|
If assign AD, automatically recovered Consolidation
operators: +-,*... |
No Shared Members |
|
No Consolidation Property. |
Required Storage Space |
|
Associated with Sparse |
Storage Property- Dynamic Calc |
|
Attributed Dimensions are below Standard Dimension. |
UDA allowed |
Difference BSO, ASO

What are the two storage options available in Essbase, and what are the differences?
Or what is the difference between BSO & ASO?
Difference BSO- ASO
|
BSO(Block Storage
Option) |
ASO(Aggregate Storage Option) |
|
1.
Write back in BSO. |
No write-back in ASO |
|
2.
Most of the Dimensions are dense
in BSO |
Most
of the dimensions are sparse in ASO |
|
3. Can create more than 1 database per Application
in BSO |
Cannot create more than 1
database per Application in ASO |
|
3. Less no. of Dimensions(between 4 and
8) in BSO |
a large number of dimensions (more than 10) in ASO |
|
4. Much suited for planning applications. |
Not much suited for planning applications. |
|
5. Calc Script/Two-Pass/Attribute Dimension |
no Calc Script/Two-Pass/Attribute Dimension |
|
6. Supports LRO |
Doesn’t Support LRO |
|
7. Convert BSO to ASO |
can’t convert ASO to BSO |
|
8. Currency Conversion
|
No Currency Conversion |
|
9. Supports- Partitions-
Linked, Transparent, Replicated |
support - Linked& Transparent |
|
10. Copy Database |
No- Copy Database |
Saturday, May 17, 2025
EPBCS Corporate Training
F or more details, Please Contact
---------------------------------------------
Job Market- Oracle EPM Cloud Modules
Job Market- Oracle EPM Cloud Modules
=================================
70%- EPBCS, PBCS Jobs
25% - FCCS, ARCS, EPCMCS
5% - EPRCS-NR, EPM Integration Agent, EDMCS
Thursday, May 15, 2025
On- Premise vs Cloud
ON- PREMISE | CLOUD |
1. Location: On-site (Your Premises) | 1. Off-Site (Host Infra.) |
2. Cost: High Cost | 2. Lower Costs |
3. Control: High control by management. | 3. Less control by host. |
4. Customization: High customization | 4. Less Customization |
5. Security: full control by management. | 5. Depend on Host. |
6. Scalability: Limited , manual | 6. High scalability |
| |
| |
| |